
SPOCC Reactor
The SPOCC Reactor combines methane, carbon dioxide and air in an electrochemical reactor. The reactions are self-sustaining at elevated temperature. The product is syngas, a platform chemical which can be converted into a huge range of chemicals. The technology is patented.
Petrochemical sites are some of the largest emitters of greenhouse gases. The SPOCC Reactor has the potential to significantly reduce emissions, and increase the product yield by converting greenhouse gases into useful products.
This is how it works:-
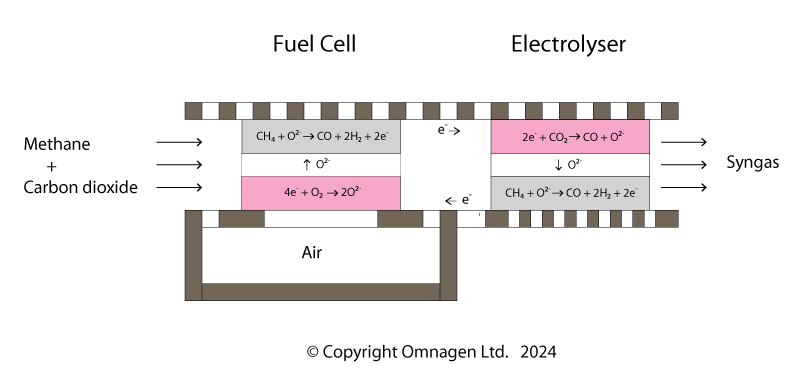
Methane reacts with air in a fuel cell, and the energy produced drives the reaction between carbon dioxide and methane in an electrolysis cell.
The SPOCC Reactor makes syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which can be used as the input for many processes, of which the major one is the Fischer-Tropsch process. This process was first developed in 1923, and converts syngas into a wide range of hydrocarbons and alcohols. If the SPOCC Reactor is added to an existing hydrogen production plant, then a truly huge range of chemicals can be made. Refer to the section on hydrogen production.
Possible applications for the SPOCC Reactor:-
- Using waste organic matter. This is fed into an anaerobic digester where it is converted into a mixture of methane and CO2. The SPOCC Reactor then converts this biogas into syngas, which has a huge range of uses. The section on biofuels provides more details.
- Linked to fossil hydrogen production, where methane and steam are converted to hydrogen and carbon dioxide. That CO2 can be mixed with more methane in a SPOCC Reactor to produce syngas, a vital source of carbon for the petrochemical industry. More information is provided here.
- Stranded natural gas assets where gas extracted in remote locations has to be converted to liquid for transportation. It often contains large amounts of carbon dioxide.
- Natural gas power stations produce vast amounts of carbon dioxide, and obviously have a supply of natural gas.
- Cement production requires heat to decompose calcium carbonate. CO2 is produced when natural gas is burnt to produce heat, and even more is produced when the carbonate decomposes.
The SPOCC Reactor uses electrochemistry, as it is the only way to harness the increase in entropy that the reactions involve. There are two components:-
- An electrolyser which reacts CO2 with methane to produce carbon monoxide plus hydrogen. This is powered by a directly linked fuel cell.
- The fuel cell reacts CO2 and methane with a separate supply of air. It produces carbon monoxide plus hydrogen, and also electricity and heat to power the electrolyser.
Please contact Ken Omersa if you'd like more information; phone and email details are provided here.
Sustainable Aviation Fuel
Anaerobic digesters convert organic matter into a mixture of methane and CO2. The SPOCC Reactor can be used as part of a route to produce sustainable aviation fuel. For an explanation.
Use Refinery Emissions
Oil refineries have a massive carbon footprint, partly through burning hydrocarbon fuels for heat, and partly as a byproduct from the chemical reactions themselves. We propose using the carbon dioxide as a raw material alongside oil and gas to make more sustainable use of available carbon resources.
Read how the SPOCC Reactor makes this possible.
Cement Decarbonisation
Cement production is responsible for at least 5% of global carbon dioxide emissions. Where a supply of natural gas is available, we propose capturing the CO2, adding natural gas and air, and making syngas at the site. This can be further processed to valuable chemicals.


